[TOC]
0x00 标准输入输出
Write-*
模块常用cmdlet命令:

[TOC]
模块常用cmdlet命令:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10Get-Command write-* -CommandType Cmdlet | Select-Object -Property Name,Version
Name Version
---- -------
Write-Debug 3.1.0.0
Write-Error 3.1.0.0
Write-Host 3.1.0.0
Write-Output 3.1.0.0
Write-Progress 3.1.0.0
Write-Verbose 3.1.0.0
Write-Warning 3.1.0.0
Write-Debug 示例 (建议实用的方法:$host.UI.WriteDebugLine())1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11PS > Write-Debug -Message "Hello 2012 !" #首次执行没有任何输出这和$DebugPreference配置有关,
#因为$DebugPreference的默认值为:SilentlyContinue。
PS > [System.Enum]::GetNames([System.Management.Automation.ActionPreference])
SilentlyContinue # 继续
Stop # 终止
Continue # 继续
Inquire # 查询
PS > $DebugPreference="stop"
PS > Write-Debug "Hello 2012"
调试: Hello 2012
Write-Debug : 已停止执行命令,因为首选项变量“DebugPreference”或通用参数被设置为 Stop。
描述:您可以通过把ForegroundColor参数指定文本的颜色,你可以通过使用BACKGROUNDCOLOR参数中指定的背景色1
2
3
4
5
6
7Write-Host
[[-Object] <Object>]
[-NoNewline]
[-Separator <Object>]
[-ForegroundColor <ConsoleColor>]
[-BackgroundColor <ConsoleColor>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Write-Host 示例1
2
3
4
5
6PS > Write-Host "Input"
Input
PS > Write-Host "no newline test " -NoNewline #写到控制台不增加新线
PS > Write-Host (2,4,6,8,10,12) -Separator ", -> " -ForegroundColor DarkGreen -BackgroundColor White #写有不同的文字和背景颜色
2, -> 4, -> 6, -> 8, -> 10, -> 12
PS > Write-host "Script Running now , please waiting it.." -ForegroundColor Green
描述: 如果命令为最后一个命令在管道中,对象显示在控制台中。1
2
3
4Write-Output
[-InputObject] <PSObject[]>
[-NoEnumerate]
[<CommonParameters>]
Write-output 示例1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14PS > Write-Output "Input" | Get-Member
Input
TypeName:System.String
# Name MemberType Definition
# ---- ---------- ----------
# Clone Method System.Object Clone(), System.Object ICloneable.Clone()
# CompareTo Method int CompareTo(System.Object value), int CompareTo(string strB), int IComparab...
# Contains Method bool Contains(string value)
# CopyTo Method void CopyTo(int sourceIndex, char[] destination, int destinationIndex, int co... E
PS > (Write-Output "Input").startsWith("I") #验证第一位开始的字符
True
PS > (Write-Output "Input").startsWith("k")
False
1 | Write-Warning [-Message] <System.String> [<CommonParameters>] |
Write-Warning 基础示例1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19PS > Write-Warning "This is only a test warning."
PS > "This is only a test warning." | Write-Warning # 警告: This is only a test warning. # 黄色输出
# 设置$WarningPreference变量并写入警告
PS> $WarningPreference
Continue
PS> Write-Warning "This is only a test warning."
This is only a test warning.
PS> $WarningPreference = "SilentlyContinue"
PS> Write-Warning "This is only a test warning."
PS> $WarningPreference = "Stop"
PS> Write-Warning "This is only a test warning."
# WARNING: This is only a test message.
# Write-Warning : Command execution stopped because the shell variable "WarningPreference" is set to Stop.
# At line:1 char:14
# + Write-Warning <<<< "This is only a test message."
PS> Write-Warning "This is only a test warning." -WarningAction Inquire # 设置WarningAction参数并写入警告
# 确认
# 是否继续执行此操作?
# [Y] 是(Y) [A] 全是(A) [H] 终止命令(H) [S] 暂停(S) [?] 帮助 (默认值为“Y”): Y
1 | Write-Error [[-Message] <System.String>] [-Category {NotSpecified | OpenError | CloseError | DeviceError | DeadlockDetected |
Write-Error 基础示例1
2
3
4
5
6# 1.错误信息提示并停止默认
Write-Error -Message "[Error] - 错误提示信息"
# 2.使用异常对象写入错误
$E = [System.Exception]@{Source="Get-ParameterNames.ps1";HelpLink="https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=113425"}
Write-Error -Exception $E -Message "Files not found. The $Files location does not contain any XML files."
1 | # 语法 |
Write-Progress 命令示例1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58# Example 1: Display the progress of a For loop
for ($i = 1; $i -le 100; $i++ )
{
# This command displays the progress of a For loop that counts from 1 to 100.
Start-Sleep 1
Write-Progress -Activity "Search in Progress" -Status "$i% Complete:" -PercentComplete $i;
}
# Example 2: Display the progress of nested For loops
for($I = 1; $I -lt 101; $I++ )
{
Write-Progress -Activity Updating -Status 'Progress->' -PercentComplete $I -CurrentOperation OuterLoop
for($j = 1; $j -lt 101; $j++ )
{
Write-Progress -Id 1 -Activity Updating -Status 'Progress' -PercentComplete $j -CurrentOperation InnerLoop
}
}
# Example 3: Display the progress while searching for a string
# 使用Get EventLog获取系统日志中的事件,并将它们存储在$events变量中。
$Events = Get-EventLog -LogName system
# Pipe the events to the ForEach-Object cmdlet.
$Events | ForEach-Object -Begin {
# In the Begin block, use Clear-Host to clear the screen.
Clear-Host
# Set the $i counter variable to zero.
$i = 0
# Set the $out variable to a empty string.
$out = ""
} -Process {
# In the Process script block search the message property of each incoming object for "bios".
if($_.message -like "*bios*")
{
# Append the matching message to the out variable.
$out=$out + $_.Message
}
# Increment the $i counter variable which is used to create the progress bar.
$i = $i+1
# Use Write-Progress to output a progress bar.
# The Activity and Status parameters create the first and second lines of the progress bar heading, respectively.
Write-Progress -Activity "Searching Events" -Status "Progress:" -PercentComplete ($i/$Events.count*100)
} -End {
# Display the matching messages using the out variable.
$out
}
# Example 4: Display progress for each level of a nested process
foreach ( $i in 1..10 ) {
Write-Progress -Id 0 "Step $i"
foreach ( $j in 1..10 ) {
Write-Progress -Id 1 -ParentId 0 "Step $i - Substep $j"
foreach ( $k in 1..10 ) {
Write-Progress -Id 2 -ParentId 1 "Step $i - Substep $j - iteration $k"; start-sleep -m 150
}
}
}

weiyigeek.top-Write-Progress
基础语法:1
Write-Information [-MessageData] <System.Object> [[-Tags] <System.String[]>] [<CommonParameters>]
基础示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35# Example 1: Write information for Get- results
Write-Information -MessageData "Got your features!" -InformationAction Continue
PS C:\Users\WeiyiGeek> Write-Information -MessageData "Got your features!" 6> 2.txt
PS C:\Users\WeiyiGeek> cat .\2.txt
Got your features!
# Example 2: Write information and tag it -----------
$message = "To filter your results for PowerShell, pipe your results to the Where-Object cmdlet."
Get-WindowsFeature -Name p*
Write-Information -MessageData $message -Tags "Instructions" -InformationAction Continue
# Display Name Name Install State
# ------------ ---- -------------
# [ ] Print and Document Services Print-Services Available
# [ ] Print Server Print-Server Available
# [ ] Distributed Scan Server Print-Scan-Server Available
# [ ] Internet Printing Print-Internet Available
# [ ] LPD Service Print-LPD-Service Available
# [ ] Peer Name Resolution Protocol PNRP Available
# [X] Windows PowerShell PowerShellRoot Installed
# [X] Windows PowerShell 5.0 PowerShell Installed
# [ ] Windows PowerShell 2.0 Engine PowerShell-V2 Removed
# [X] Windows PowerShell ISE PowerShell-ISE Installed
# To filter your results for PowerShell, pipe your results to the Where-Object cmdlet.
# Example 3: Write information to a file ------------
function Test-Info
{
Get-Process P*
Write-Information "Here you go"
}
Test-Info 6> Info.txt
PS C:\Users\WeiyiGeek> Get-Content .\Info.txt
Here you go
其它方式补充输出:1
2
3
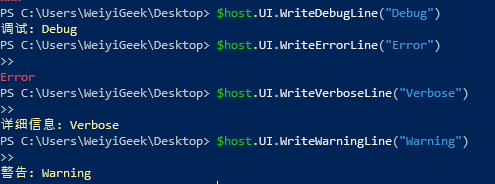
4$host.UI.WriteDebugLine("Debug") #调试: Debug
$host.UI.WriteErrorLine("Error") #Error
$host.UI.WriteVerboseLine("Verbose") #详细信息: Verbose
$host.UI.WriteWarningLine("Warning") #警告: Warning
weiyigeek.top-Write
基础 cmdlet 一览:
基础语法:1
2# 语法
Out-File [-FilePath] <System.String> [[-Encoding] {ASCII | BigEndianUnicode | Default | OEM | String | Unicode | Unknown | UTF7 | UTF8 | UTF32}] [-Append] [-Force] [-InputObject <System.Management.Automation.PSObject>] [-NoClobber] [-NoNewline] [-Width <System.Int32>] [-Confirm] [-WhatIf] [<CommonParameters>]
Out-File 示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23# Example 1: Send output and create a file
dir | Out-File .\ls.html
Get-Process | Out-File -FilePath .\Process.txt
# Example 2:防止覆盖现有文件
Get-Process | Out-File -FilePath .\Process.txt -NoClobber
# Example 3: 以ASCII格式将输出发送到文件
$Procs = Get-Process
Out-File -FilePath .\Process.txt -InputObject $Procs -Encoding ASCII -Width 50
# Example 4: 使用提供程序并将输出发送到文件
PS> Set-Location -Path Alias: # 设置到本地路径为别名
PS> Get-Location
# Path
# ----
# Alias:\
PS> Get-ChildItem | Out-File -FilePath C:\TestDir\AliasNames.txt # 此处Get-ChildItem获取的应该是别名相关信息。
PS> Get-Content -Path C:\TestDir\AliasNames.txt
# CommandType Name
# ----------- ----
# Alias % -> ForEach-Object
Set-Location -Path $home # 还原本地路径为家目录
描述: 该Out-Hostcmdlet将输出发送到PowerShell主机进行显示。
基础语法1
2
3
4
5
6Out-Host
[-Paging]
[-InputObject <PSObject>]
[<CommonParameters>]
# Paging参数一次显示一页数据。
Out-Host 示例1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9# 示例1.一次显示一页输出
PS > pwd; Get-Service | Out-Host -paging
PS > dir | Out-Host -paging
<SPACE> 下一页;<CR> 下一行;Q 退出
# 示例2.使用变量作为输入
# Out-Host使用InputObject参数指定$io变量并显示历史记录。
$io = Get-History # 与 Linux中的history命令相似
Out-Host -InputObject $io
描述:默认情况下会Out-String 累积字符串并将其作为单个字符串返回,但是您可以使用Stream 参数直接指示一次Out-String返回一行,也可以创建字符串数组。当对象操作不太方便时,可以使用此cmdlet像在传统shell中一样搜索和操作字符串输出。
基础语法:1
2
3
4
5
6Out-String
`[-Stream]`
[-Width <Int32>]
[-NoNewline ]
[-InputObject <PSObject>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Out-String 示例1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32# 1.取当前区域性并将数据转换为字符串
PS > ipconfig | Out-String
# 宽度参数被设置为每行256个字符以防止截断。
PS > Out-String -InputObject (ls) -Width 256
# 目录:
# Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
# ---- ------------- ------ ----
# d----- 2019/7/26 8:45 .android
PS> @{TestKey = ('x' * 200)} | Out-String
# Name Value
# ---- -----
# TestKey xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx...
PS> @{TestKey = ('x' * 200)} | Out-String -Width 250
# Name Value
# ---- -----
# TestKey xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
# xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
# xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
# 2.将对象数据转换为字符串
$C = Get-Culture | Select-Object -Property *
Out-String -InputObject $C -Width 100
# 3.要查看Out-String数组,请将输出存储到变量,然后使用数组索引查看元素。
$str = Out-String -InputObject $C -Width 100
# 4.使用对象和使用字符串之间的区别
# Out-String 使用 Stream 参数 将每个对象转换为字符串,而不是将所有对象串联为单个字符串
Get-Alias | Out-String -Stream | Select-String -Pattern "gcm"
Alias gcm -> Get-Command
描述: 该Out-Printercmdlet将输出发送到默认打印机或另一台打印机(如果已指定)。
基础语法:1
2
3
4Out-Printer
[[-Name] <String>]
[-InputObject <PSObject>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Out-Printer 示例1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13# 1.将当前目录的内容发送到默认打印机上
dir | Out-Printer
# 2.Get-Content获取readme.txt当前目录中文件的内容Out-Printer并将其通过管道传输到 ,然后将其发送到默认打印机。
Get-Content -Path ./readme.txt | Out-Printer
# 3.本示例将打印Hello, World到Server01上的Prt-6B彩色打印机。
"Hello, World" | Out-Printer -Name "\\Server01\Prt-6B Color"
# 4.本示例将输出的完整版本的“帮助”主题Get-CimInstance打印到默认打印机
$H = Get-Help -Full Get-CimInstance
Out-Printer -InputObject $H
基础描述: 所述外空小命令将其输出发送到NULL,实际上从管道中取出,并防止所述输出在屏幕上显示。
基础语法: Out-Null [-InputObject <PSObject>] [<CommonParameters>]
Tips : 类似于Linux上执行的数据回收站,例如 echo "我是被销毁的数据" > /dev/null && cat /dev/null
Out-Null 示例1
2
3# 1.命令Out-Null 或 >$null 吸收输出(删除)结果。
dir | Out-Null
dir > $null
描述: PowerShell会自动添加Out-Default到每个管道的末尾,它决定如何格式化和输出对象流。
基础语法1
2
3
4Out-Default
[-Transcript]
[-InputObject <PSObject>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Out-Default 示例1
2
3
4
5PS > ls | Out-Default
PS > & { pwd;Get-Service} | Out-Default
# Status : Running
# Name : XLServicePlatform
# DisplayName : 迅雷下载基础服务(用于快速申请磁盘空间及接管浏览器下载请求)
描述: 该 Out-GridView (别名 ogv) cmdlet将命令的输出发送到网格视图窗口(注意需要界面),在该窗口中输出显示在交互式表中。
您可以使用表的以下功能来检查数据:
基础语法:1
2
3
4
5Out-GridView
[-InputObject <PSObject>]
[-Title <String>]
[-PassThru] | [-OutputMode <OutputModeOption>] | [-Wait]
[<CommonParameters>]
Out-GridView 示例1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20# 示例1.将过程输出到网格视图(方便进行排序过滤)
Get-Process | Out-GridView
# 示例2.使用变量将过程输出到网格视图
$P = Get-Process
$P | Out-GridView
# 示例3.在网格视图中显示选定的属性
Get-Process | Select-Object -Property Name, WorkingSet, PeakWorkingSet |
Sort-Object -Property WorkingSet -Descending | Out-GridView
# 示例4:将输出保存到变量,然后输出网格视图
($A = Get-ChildItem -Path $PSHOME -Recurse) | Out-GridView -Title "Filder Item"
# 示例5:通过`Out-GridView`传递多个项目
# 的PassThru参数Out-GridView使您可以沿管道发送多个项目。该的PASSThru参数等同于使用多的价值输出outputmode 参数。
Get-Process | Out-GridView -PassThru | Export-Csv -Path .\ProcessLog.csv
# 示例6:创建Windows到`Out-GridView`的快捷方式
pwsh -Command "Get-Service | Out-GridView -Wait"
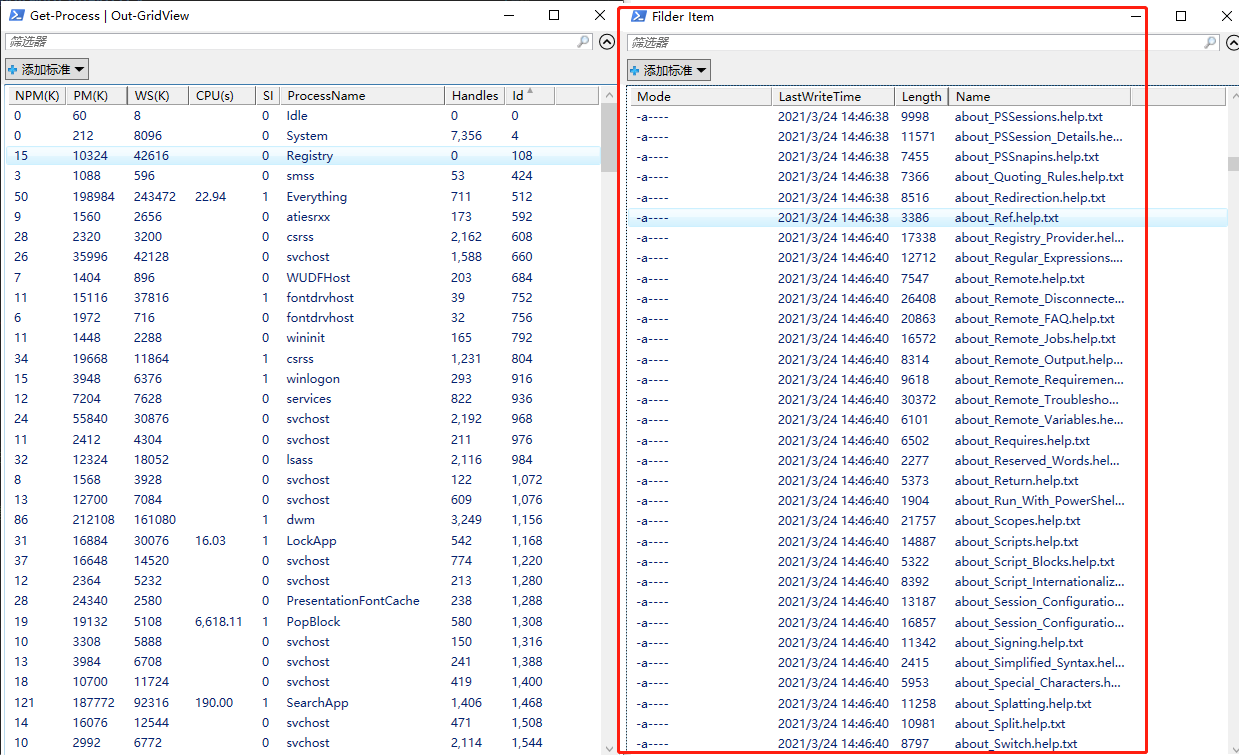
weiyigeek.top-GridView
描述:可以将管道中的对象进行格式化后字符后进行输出展示,采用Get-Command -Verb format的命令,查看所有以Format打头的命令;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8Get-Command -Verb format | where {$_.Source -eq "Microsoft.PowerShell.Utility" }
CommandType Name Version Source
----------- ---- ------- ------
Function Format-Hex 3.1.0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.Utility
Cmdlet Format-Custom 3.1.0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.Utility
Cmdlet Format-List 3.1.0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.Utility
Cmdlet Format-Table 3.1.0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.Utility
Cmdlet Format-Wide 3.1.0.0 Microsoft.PowerShell.Utility
描述: 对于任何一个对象都可以使用Format-List *查看它所有的属性和方法。
基础语法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10# 对于任何一个对象都可以使用Format-List * , 查看它所有的属性和方法。
Format-List
[[-Property] <Object[]>]
[-GroupBy <Object>]
[-View <string>]
[-ShowError][-DisplayError]
[-Force]
[-Expand <string>]
[-InputObject <psobject>]
[<CommonParameters>]
基础示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36# 1.Format-List基础案例
PS > Get-process | Format-List
# Id : 3108
# Handles : 196
# CPU :
# SI : 0
# Name : wsctrl
PS > Get-process | Format-List -Property Name
# Name : wsctrl
# 2.以列表的形式查看对象它所有的属性和方法并以分页的形式输出。
PS > ls | Format-List * | Out-Host -Paging
# PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\FileSystem::\.android
# PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\FileSystem::
# PSChildName : .android
# PSDrive : C
# PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\FileSystem
# PSIsContainer : True
# Mode : d-----
# BaseName : .android
# Target : {}
# LinkType :
# Name : .android
# FullName : \.android
# Parent : WeiyiGeek
# Exists : True
# Root : C:\
# Extension : .android
# CreationTime : 2019/7/26 8:45:03
# CreationTimeUtc : 2019/7/26 0:45:03
# LastAccessTime : 2019/7/26 8:45:03
# LastAccessTimeUtc : 2019/7/26 0:45:03
# LastWriteTime : 2019/7/26 8:45:03
# LastWriteTimeUtc : 2019/7/26 0:45:03
# Attributes : Directory
# <SPACE> 下一页;<CR> 下一行;Q 退出
基础语法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14Format-Table
[-AutoSize]
[-RepeatHeader]
[-HideTableHeaders]
[-Wrap]
[[-Property] <Object[]>]
[-GroupBy <Object>]
[-View <String>]
[-ShowError]
[-DisplayError]
[-Force]
[-Expand <String>]
[-InputObject <PSObject>]
[<CommonParameters>]
基础实例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47# 1.显示指定的属性
PS > Get-process | Format-Table -Property Handle,Name -AutoSize
# Handle Name
# ------ ----
# 5544 ApplicationFrameHost
PS > ls | Format-Table Name,Length,LastWriteTime
# 查看当前以i打头的进程,并显示进程的名字和其它以”pe”打头,以”64″结尾的进程。
PS > Get-Process i* | Format-Table Name,pe*64
# 2.因为属性和属性的内容太多可能不会显示完全,可以使用文本换行参数
PS > ls | Format-Table *
# 换行显示并且通过-AutoSize参数对列的宽带进行优化,会将属性值的最大宽带作为每一列的宽度
PS > ls | Format-Table * -Wrap -AutoSize
# 3.脚本块作为属性
# 在Powershell中文件的Length默认以byte作为单位如果你象让它输出时以KB显示
PS > ls | Format-Table Name,{ [int]($_.Length/1kb) } -Wrap
# 4.修改列标题
# 方式1.可以使用Lable设置显示列头为KB而不是[int]($_.Length/1kb)
PS > ls | Format-Table Name,@{ Expression={[int]($_.Length/1kb)};Label="Kb"} -Wrap
# Name KB
# ---- ----------------------
# .gitconfig 0
# .viminfo 8
# .vimrc 11
# 方式2
PS > $column1 = @{expression="Name"; width=30;label="filename"; alignment="left"}
PS > $column2 = @{expression="LastWriteTime"; width=40;label="last modification"; alignment="right"}
PS > ls | Format-Table $column1, $column2
# filename last modification
# -------- -----------------
# .android 2019/7/26 8:45:03
# .config 2019/8/19 17:27:45
# 5.GroupBy的参数完成分组统计
ls | Sort-Object Extension, Name | Format-Table -groupBy Extension
# 目录: C:Powershell
# Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
# ---- ------------- ------ ----
# -a--- 2011/11/24 20:26 12060 alias
# .......
基础示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13# Example 1: 格式化当前目录中的文件名
Get-ChildItem | Format-Wide -Column 3
# Example 2: 设置注册表项名称的格式
Get-ChildItem HKCU:\software\microsoft | Format-Wide -Property pschildname -AutoSize
# Example 3: 格式错误疑难解答
PS /> Get-Date | Format-Wide { $_ / $null } -DisplayError
#ERR
PS /> Get-Date | Format-Wide { $_ / $null } -ShowError
# Failed to evaluate expression " $_ / $null ".
# + CategoryInfo : InvalidArgument: (12/21/2018 8:18:01 AM:PSObject) [], RuntimeException
# + FullyQualifiedErrorId : PSPropertyExpressionError
描述: 在格式-定制小命令格式化为以交替的视图定义的命令的输出
基础语法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12# 语法
Format-Custom
[[-Property] <Object[]>]
[-Depth <Int32>]
[-GroupBy <Object>]
[-View <String>]
[-ShowError] #通过管道发送错误
[-DisplayError]
[-Force]
[-Expand <String>]
[-InputObject <PSObject>]
[<CommonParameters>]
基础示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41# 0.默认输入与Format-Custom比较案例
Get-Process Winlogon
# Handles NPM(K) PM(K) WS(K) CPU(s) Id SI ProcessName
# ------- ------ ----- ----- ------ -- -- -----------
# 272 12 2900 12024 932 1 winlogon
PS D:\> Get-Process Winlogon | Format-Custom
class Process
# {
# Id = 932
# Handles = 272
# CPU =
# SI = 1
# Name = winlogon
# }
# Example 1: 使用自定义视图格式化输出
# 此命令将有关“Start-Transcript”cmdlet的信息格式化为MyView视图定义的格式,MyView视图是用户创建的自定义视图。
Get-Command Start-Transcript | Format-Custom -View MyView
# Example 2: 使用默认视图格式化输出
# 此命令在另一个自定义视图中格式化有关Winlogon进程的信息。
Get-Process Winlogon | Format-Custom
# Example 3: 格式错误疑难解答
PC /> Get-Date | Format-Custom DayOfWeek,{ $_ / $null } -DisplayError
class DateTime {
DayOfWeek = Friday
$_ / $null = #ERR
}
PC /> Get-Date | Format-Custom DayOfWeek,{ $_ / $null } -ShowError
class DateTime {
DayOfWeek = Friday
$_ / $null =
}
# Failed to evaluate expression " $_ / $null ".
# + CategoryInfo : InvalidArgument: (12/21/2018 8:01:04 AM:PSObject) [], RuntimeException
# + FullyQualifiedErrorId : PSPropertyExpressionError
基础实例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12# 语法
Format-Hex
-InputObject <System.Object>
[-Encoding {ASCII | BigEndianUnicode | Unicode | UTF7 | UTF8 | UTF32}]
[-Count <long>]
[-Offset <long>]
[-Raw]
[<CommonParameters>]
Format-Hex -LiteralPath <System.String[]> [<CommonParameters>]
Format-Hex [-Path] <System.String[]> [<CommonParameters>]
基础语法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19# 1.Format-Hex 将文字或者文件转换成为十六进制数据
PS> 'WeiyiGeek' | Format-Hex
#00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F
#00000000 57 65 69 79 69 47 65 65 6B WeiyiGeek
PS> Format-Hex -Path .\File.t7f
# Path: C:\Test\File.t7f
# 00000000 25 50 44 46 2D 31 2E 35 0D 0A 25 B5 B5 B5 B5 0D %PDF-1.5..%????.
# 2.显示原始十六进制输出
PS> 1,2,3,1000 | Format-Hex
Path: 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F
00000000 01 02 03 E8 03 ...è.
# 3.注意输出的不同。Raw参数将数字显示为4字节值,与Int32类型相同。
PS> 1,2,3,1000 | Format-Hex -Raw
Path: 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F
00000000 01 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 03 00 00 00 E8 03 00 00 ............è...
你好看友,欢迎关注博主微信公众号哟! ❤
这将是我持续更新文章的动力源泉,谢谢支持!(๑′ᴗ‵๑)
温馨提示: 未解锁的用户不能粘贴复制文章内容哟!
方式1.请访问本博主的B站【WeiyiGeek】首页关注UP主,
将自动随机获取解锁验证码。
Method 2.Please visit 【My Twitter】. There is an article verification code in the homepage.
方式3.扫一扫下方二维码,关注本站官方公众号
回复:验证码
将获取解锁(有效期7天)本站所有技术文章哟!

@WeiyiGeek - 为了能到远方,脚下的每一步都不能少
欢迎各位志同道合的朋友一起学习交流,如文章有误请在下方留下您宝贵的经验知识,个人邮箱地址【master#weiyigeek.top】或者个人公众号【WeiyiGeek】联系我。
更多文章来源于【WeiyiGeek Blog - 为了能到远方,脚下的每一步都不能少】, 个人首页地址( https://weiyigeek.top )

专栏书写不易,如果您觉得这个专栏还不错的,请给这篇专栏 【点个赞、投个币、收个藏、关个注、转个发、赞个助】,这将对我的肯定,我将持续整理发布更多优质原创文章!。
最后更新时间:
文章原始路径:_posts/编程世界/Powershell/Cmdlet/编程脚本类命令/PS常用命令之脚本编程常用命令.md
转载注明出处,原文地址:https://blog.weiyigeek.top/2019/12-21-321.html
本站文章内容遵循 知识共享 署名 - 非商业性 - 相同方式共享 4.0 国际协议