[TOC]
ansbile 循环 在使用ansible的过程中,我们经常需要处理一些返回信息而这些返回信息中,通常可能不是单独的一条返回信息而是一个信息列表;
循环常用关键字:
with_items : 迭代列表里面的值或者变量的结果,不分层次全部输出
with_list : 会循环的输出列表(最外层大列表)中的每一项,分层次
with_flattened : 与items相同将嵌套列表”拉平展开”,循环的处理每个元素
with_together : 将两个列表中的元素”对齐合并-一一对应
with_cartesian : 将每个小列表中的元素按照”笛卡尔的方式”组合后,循环的处理每个组合
with_nested : 与cartesian相同将每个小列表中的元素按照”笛卡尔的方式”组合
with_indexed_items : 根据列表设置索引值,可根据索引值取值
with_sequence : 迭代序列选择步长和输出指定格式话
with_random_choice : 列表中随机返回一个值
with_dict : 遍历字典key与value
with_subelements : 遍历复合结构的字典属性
with_file : 读取ansible主机中的文件中内容并且遍历
with_fileglob : 读取ansible主机中指定的目录中匹配符合模式的文件名,只包括文件不包括目录;
with_items 关键字 如果我们想要循环的处理信息列表中的每一条信息,我们该怎么办呢? 即"with_items"关键字会把返回的列表信息自动处理,将每一条信息单独放在一个名为”item”的变量中,我们只要获取到名为”item”变量的变量值,即可循环的获取到列表中的每一条信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 tasks: - debug: msg: "{{item}}" with_items: [ 1, 2, 3 ] tasks: - debug: msg: "{{item}}" with_items: [ 1, 2, 3 ] tasks: - debug: msg: "{{item.test1}}" with_items: - { test1: a, test2: b } - { test1: c, test2: d } - debug: msg: "{% for i in item %} {{ i }} {% endfor %}" with_items : [ 1, 2, 3 ]
示例1:如果我想要获取到清单中所有分组的主机的主机名,并且获取返回信息中的第二条信息;1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 ansible testA -m debug -a "msg={{groups.all}}" ansible testA -m debug -a "msg={{groups.all[1]}}"
实际演示:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 --- - hosts: local remote_user: root gather_facts: no tasks: - debug: msg: "{{item}} " with_items: "{{groups.all}} " - debug: msg: "{% for i in item %}{{ i }} {% endfor %}" with_items : ["1","2","3"] END ansible-playbook withitems.yml TASK [debug] ok: [local] => (item=local) => { "msg": "local" } ok: [local] => (item=10.10.107.221) => { "msg": "10.10.107.221" } ok: [local] => (item=10.20.172.179) => { "msg": "10.20.172.179" } TASK [debug] ok: [local] => (item=1) => { "msg": "1" } ok: [local] => (item=2) => { "msg": "2" } ok: [local] => (item=3) => { "msg": "3" }
比如,在没有学会使用循环之前如果想要在同一主机中创建四个文件,但是学了循环后您只需要将建立的文件放入数组之中,然后迭代使用;
循环常使用案例:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 --- - hosts: local remote_user: root gather_facts: no vars: dirs: - "/tmp/a" - "/tmp/b" - "/tmp/c" - "/tmp/d" tasks: - file: path: "{{item}} " state: touch with_items: "{{dirs}} " - shell: "whoami" register: "cmd" - debug: msg: "{{cmd[item]}} " with_items: "{{cmd}} " - debug: var: cmd[item] with_items: "{{cmd}} " END
(1)示例执行结果:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 TASK [file] changed: [local ] => (item=/tmp/a) changed: [local ] => (item=/tmp/b) changed: [local ] => (item=/tmp/c) changed: [local ] => (item=/tmp/d) TASK [debug] ok: [local ] => (item=changed) => { "msg" : true } ok: [local ] => (item=stdout) => { "msg" : "root" } ok: [local ] => (item=delta) => { "msg" : "0:00:00.022253" } ok: [local ] => (item=stdout_lines) => { "msg" : ["root" ] } ok: [local ] => (item=end) => { "msg" : "2019-08-01 10:47:41.760052" } ok: [local ] => (item=start) => { "msg" : "2019-08-01 10:47:41.737799" } ok: [local ] => (item=cmd) => { "msg" : "whoami" } ok: [local ] => (item=failed) => { "msg" : false } ok: [local ] => (item=changed) => { "ansible_loop_var" : "item" , "cmd[item]" : true , "item" : "changed" } ok: [local ] => (item=stdout) => { "ansible_loop_var" : "item" , "cmd[item]" : "root" , "item" : "stdout" } ....... 其他忽略
采用循环我们也可以像file模块一样执行多个命令,只需要将要执行的命令放入with_items关键字中;
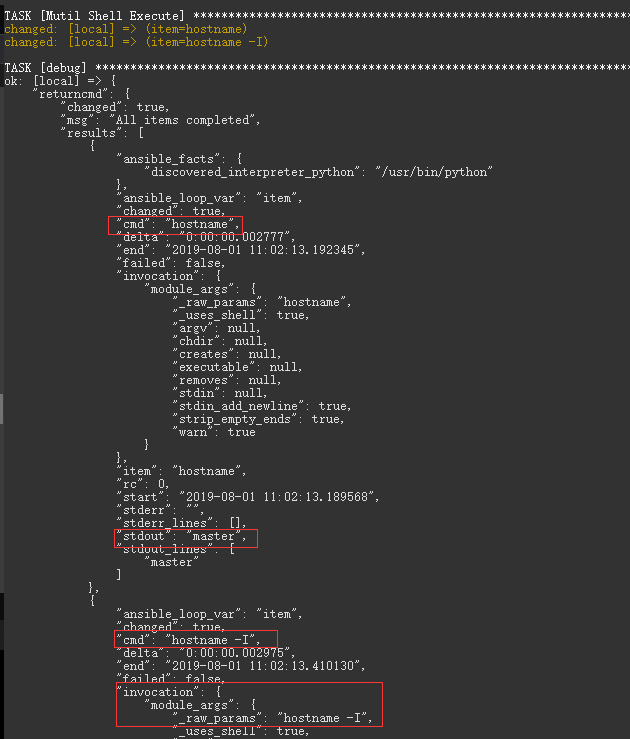
循环输出方式2:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 --- - hosts: local remote_user: root vars: cmd: - "hostname" - "hostname -I" gather_facts: no tasks: - name: "Mutil Shell Execute" shell: "{{item}} " with_items: "{{cmd}} " register: returncmd - debug: var: returncmd - name: "show shell execute result" debug: msg: "{{item.stdout}} " with_items: "{{returncmd.results}} " - name: "jinja2 syntax" debug: msg: "{% for i in returncmd.results %} {{ i.stdout }} {% endfor %}" END TASK [show shell execute result] ok: [local] => (item={'stderr_lines': [], .... , 'stdout_lines' : [u'master'], u'start': u'2019-08-01 11 :17:55.900489'}) => { "msg": "master" } ok: [local] => (item={'stderr_lines': [], ..... , 'stdout_lines' : [u'10.10.107.222 192.168 .1 .99 '], u' start': u'2019-08-01 11 :17:56.116440'}) => { "msg": "10.10.107.222 192.168.1.99 " } TASK [jinja2 syntax] ok: [local] => { "msg": " master 10.10.107.222 192.168.1.99 " }
weiyigeek.top-returncmd
with_list 关键字 前面我们说 with_items 会循环的输出列表(最外层大列表)中的每一项,按照之前的思路debug模块应该会将每个小列表作为一个小整体输出,而不应该输出小列表中的每个元素,但是事实却是with_items将嵌套在大列表中的每个小列表都\”展开\”了,并且将小列表中的元素都输出了
如果我们想要将每个小列表作为一个整体输出该怎么办呢? 而不会像with_items一样将小列表"展开拉平"后一并将小列表中的元素循环输出。
with_list语法:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 with_list: - [ 1, 2, 3 ] - [ a, b ] with_list: - - 1 - 2 - 3 - - a - b
with_list关键字与with_items 与 with_flattened 关键字区别示例:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 --- - hosts: local remote_user: root gather_facts: no tasks: - name: " with_list show" debug: msg: "{{item}} " with_list: - [ 1 , 2 ] - [ a, b ] - name: " with_items show" debug: msg: "{{item}} " with_items: - [ 1 , 2 ] - [ a, b ] - name: " with_flattened show" debug: msg: "{{item}} " with_flattened: - [ 1 , 2 ] - [ a, b ] END
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 TASK [with_list show] TASK [with_items show / with_flattened show]
总结:
当处理单层的简单列表时with_list与with_items以及没有任何区别,with_flattened 只有在处理"嵌套列表"时才会体现出区别;
with_items会将嵌套在内的小列表”拉平”,拉平后循环处理所有元素
with_list则不会”拉平”嵌套的列表,只会循环的处理列表(最外层列表)中的每一项。
with_flattened 与 with_items效果完全相同,将嵌套列表”拉平展开”,循环的处理每个元素
with_together 关键字 描述:目前为止我们了解了三个关键字可以用于循环操作,它们是with_list、with_items、with_flattened,下面引出一个新的关键字 with_together 将两个列表中的元素"对齐合并-一一对应"
playbook(剧本案例):1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 --- - hosts: local remote_user: root gather_facts: no tasks: - debug: msg: "{{ item }} " with_together: - [ 1 , 2 , 3 ] - [ a, b ] END
从上述结果可以看出:
第一个小列表中的第1个值与第二个小列表中的第1个值合并在一起输出了
第一个小列表中的第2个值与第二个小列表中的第2个值合并在一起输出了
第一个小列表中的第3个值与第二个小列表中的第3个值合并在一起输出了
如果元素数量不同的小列表使用with_together对齐合并,不存在列表中对应值将变成NULL;1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 ok: [local ] => (item=[None, u'c' ]) => { "msg" : [ null, "c" ] } ok: [local ] => (item=[3, None]) => { "msg" : [ 3, null ]
with_cartesian 关键字 描述:”with_cartesian”关键字的作用就是将每个小列表中的元素按照”笛卡尔的方式”组合后,循环的处理每个组合;其实还有一个关键字可以代替”with_cartesian”,它就是"with_nested"与"with_cartesian"的效果一致;
比如:我们要再{a,b,c}目录下分别建立下面两个目录{test1, test2},常规的用法可以采用# mkdir -p {a,b,c}/{test1,test2}命令,再ansible采用shell模块执行:# ansible test70 -m shell -a "mkdir -p /testdir/testdir/{a,b,c}/{test1,test2}"
但我们这里需要采用with_cartesian关键来实现上述效果:
weiyigeek.top-
实际案例:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 --- - hosts: local remote_user: root gather_facts: no tasks: - name: "Show Create directory" debug: msg: "{{ item }} " with_cartesian: - [a, b, c] - [test1, test2] - name: "shell create Directory" file: path: "/tmp/{{item.0}} /{{item.1}} " state: directory with_cartesian: - [a, b, c] - [test1, test2] END
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 TASK [Show Create directory] ok: [local ] => (item=[u'a' , u'test1' ]) => {"msg" : ["a" ,"test1" ]} ok: [local ] => (item=[u'a' , u'test2' ]) => {"msg" : ["a" , "test2" ]} ok: [local ] => (item=[u'b' , u'test1' ]) => {"msg" : ["b" ,"test1" ]} ok: [local ] => (item=[u'b' , u'test2' ]) => {"msg" : ["b" ,"test2" ]} ok: [local ] => (item=[u'c' , u'test1' ]) => {"msg" : ["c" ,"test1" ]} ok: [local ] => (item=[u'c' , u'test2' ]) => {"msg" : ["c" ,"test2" ]} TASK [shell create Directory] ok: [local ] => (item=[u'a' , u'test1' ]) ok: [local ] => (item=[u'a' , u'test2' ]) ok: [local ] => (item=[u'b' , u'test1' ]) ok: [local ] => (item=[u'b' , u'test2' ]) ok: [local ] => (item=[u'c' , u'test1' ]) ok: [local ] => (item=[u'c' , u'test2' ])
with_indexed_items 关键字 描述:顾名思义应该与”索引”有关,”with_indexed_items”的作用就是在循环处理列表时为列表中的每一项添加"数字索引","索引"从0开始.
单层列表 :按照顺序进行从0开始编号
多层列表 :会将嵌套的两层列表”拉平”后按照顺序为每一项编号,”拉平”效果跟之前总结的”with_flattened”效果类似;
但是当多加了一层嵌套以后”with_indexed_items”并不能像”with_flattened”一样将嵌套的列表”完全拉平”,第二层列表中的项如果仍然是一个列表"with_indexed_items"则不会拉平这个列表,而是将其当做一个整体进行编号。
基础示例:单层列表与多层列表1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 --- - hosts: local remote_user: root gather_facts: no tasks: - name: "Example play 1" debug: msg: "E.g 1: index is : {{ item.0 }} , value is {{ item.1 }} " with_indexed_items: - test1 - test2 - test3 - name: "Example play 2" debug: msg: "E.g 2: index is : {{ item.0 }} , value is {{ item.1 }} " with_indexed_items: - [a,b,c] - [test1, test2] - name: "Example play 3" debug: msg: "E.g 3: index is : {{ item.0 }} , value is {{ item.1 }} " with_indexed_items: - [a,b] - [c, [d,e]] - [end] END
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 ok: [local ] => (item=[0, u'test1' ]) => {"msg" : "E.g 1: index is : 0 , value is test1" } ok: [local ] => (item=[1, u'test2' ]) => {"msg" : "E.g 1: index is : 1 , value is test2" } ok: [local ] => (item=[2, u'test3' ]) => {"msg" : "E.g 1: index is : 2 , value is test3" } ok: [local ] => (item=[0, u'a' ]) => {"msg" : "E.g 2: index is : 0 , value is a" ok: [local ] => (item=[1, u'b' ]) => {"msg" : "E.g 2: index is : 1 , value is b" } ok: [local ] => (item=[2, u'c' ]) => {"msg" : "E.g 2: index is : 2 , value is c" } ok: [local ] => (item=[3, u'test1' ]) => {"msg" : "E.g 2: index is : 3 , value is test1" } ok: [local ] => (item=[4, u'test2' ]) => {"msg" : "E.g 2: index is : 4 , value is test2" } ok: [local ] => (item=[0, u'a' ]) => {"msg" : "E.g 3: index is : 0 , value is a" } ok: [local ] => (item=[1, u'b' ]) => {"msg" : "E.g 3: index is : 1 , value is b" } ok: [local ] => (item=[2, u'c' ]) => {"msg" : "E.g 3: index is : 2 , value is c" } ok: [local ] => (item=[3, [u'd' , u'e' ]]) => {"msg" : "E.g 3: index is : 3 , value is [u'd', u'e']" } ok: [local ] => (item=[4, u'end' ]) => {"msg" : "E.g 3: index is : 4 , value is end" }
with_sequence 关键字 描述:采用with_sequence关键字,可以指定开始与结束并且可以指定step步跳,即可以帮助我们按照顺序生成数字序列;"with_sequence"还有一个小功能,就是\”格式化\”输出数据的功能,\”格式化数据\”的方法与C语言的printf函数的使用方法类似,
基础案例:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 --- - hosts: local remote_user: root gather_facts: no tasks: - name: "Method 1" debug: msg: "{{ item }}" with_sequence: start=1 end=3 stride=1 - name: "Method 2" debug: msg: "{{ item }}" with_sequence: count=3 - name: "Demo 3" debug: msg: "{{ item }}" with_sequence: start=6 end=2 stride=-2 format="number is %0.2f" - name: "Demo 4 - Create dir" file: path: "/tmp/test{{ item }}" state: directory with_sequence: start=2 end=10 stride=2 END
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 ok: [local ] => (item=1) => {"msg" : "1" } ok: [local ] => (item=2) => {"msg" : "2" } ok: [local ] => (item=3) => {"msg" : "3" } ok: [local ] => (item=number is 6.00) => {"msg" : "number is 6.00" } ok: [local ] => (item=number is 4.00) => {"msg" : "number is 4.00" } ok: [local ] => (item=number is 2.00) => {"msg" : "number is 2.00" } changed: [local ] => (item=2) changed: [local ] => (item=4) changed: [local ] => (item=6) changed: [local ] => (item=8) changed: [local ] => (item=10)
总结:
当我们不指定stride的值时,stride的值默认为1;
当end的值小于start的值时,则必须指定stride的值,而且stride的值必须是负数;
with_random_choice 关键字 描述:可以从列表的多个值中随机返回一个值;
我们使用\”with_random_choice\”处理这个列表,可以看出每次返回的结果是从列表中随机选中的一个1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 --- - hosts: local remote_user: root gather_facts: no tasks: - debug: msg: "{{ item }}" with_random_choice: - "one" - 2 - "three" - 4 - "five" END TASK [debug] ok: [local ] => (item=three) => { "msg" : "three" }
with_dict 关键字 描述:从字面意思就可看出,它是可以遍历对象的即字典类型的,分别将字典的key与value进行存储并且支持迭代;
基础案例:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 --- - hosts: local remote_user: root gather_facts: no vars: users: WeiyiGeek: female Baby_ang: male tasks: - name: "Demo 1.dict" debug: msg: "Username: {{ item.key }} , User's gender: {{ item.value }}" with_dict: "{{users}}" - name: "Demo 2.dict" debug: msg: "Item: {{ item.key }}, Username: {{ item.value['name'] }} , User's gender: {{ item.value.gender }} , User's Telephone: {{ item.value.telephone }}" with_dict: alice: name: Alice Appleworth gender: female telephone: 123-456-7890 bob: name: Bob Bananarama gender: male telephone: 987-654-3210 END
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 ok: [local ] => (item={'value' : u'male' , 'key' : u'Baby_ang' }) => { "msg" : "Username: Baby_ang , User's gender: male" } ok: [local ] => (item={'value' : u'female' , 'key' : u'WeiyiGeek' }) => { "msg" : "Username: WeiyiGeek , User's gender: female" } ok: [local ] => (item={'value' : {u'gender' : u'male' , u'name' : u'Bob Bananarama' , u'telephone' : u'987-654-3210' }, 'key' : u'bob' }) => { "msg" : "Item: bob, Username: Bob Bananarama , User's gender: male , User's Telephone: 987-654-3210" } ok: [local ] => (item={'value' : {u'gender' : u'female' , u'name' : u'Alice Appleworth' , u'telephone' : u'123-456-7890' }, 'key' : u'alice' }) => { "msg" : "Item: alice, Username: Alice Appleworth , User's gender: female , User's Telephone: 123-456-7890" }
with_subelements 关键字 描述:该关键字支持复合类型的字典;”with_subelements”的以处理一个的复合结构的字典数据,在处理这个字典的同时,需要指定一个子元素,这个子元素的值必须是一个列表,”with_subelements”会将子元素的列表中的每一项作为一个整体,将其他子元素作为一个整体,然后将两个整体组合成item。
基础案例:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 --- - hosts: local remote_user: root gather_facts: no vars: users: - name: WeiyiGeek gender: male hobby: - Skateboard - VideoGame - name: Xiaodaigua gender: female hobby: - Music tasks: - debug: msg: "{{ item.0.name }} 's hobby is {{ item.1 }} , User's Gender is {{ item.0.gender}}" with_subelements: - "{{users}}" - hobby END
执行结果:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ok: [local ] => (item=[{u'gender' : u'male' , u'name' : u'WeiyiGeek' }, u'Skateboard' ]) => { "msg" : "WeiyiGeek 's hobby is Skateboard , User's Gender is male" } ok: [local ] => (item=[{u'gender' : u'male' , u'name' : u'WeiyiGeek' }, u'VideoGame' ]) => { "msg" : "WeiyiGeek 's hobby is VideoGame , User's Gender is male" } ok: [local ] => (item=[{u'gender' : u'female' , u'name' : u'Xiaodaigua' }, u'Music' ]) => { "msg" : "Xiaodaigua 's hobby is Music , User's Gender is female" }
with_file 关键字 描述:循环的获取到ansible主机中的文件的内容,注意不是远程目标主机中的文件;
基础示例:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 --- - hosts: local remote_user: root gather_facts: no tasks: - debug: msg: "{{ item }}" with_file: - /tmp/demo1.txt - /tmp/demo2.txt END
执行结果:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ok: [local ] => (item=.....) => { "msg" : "master\n10.10.107.222 192.168.1.99 \nMon Aug 5 16:29:39 CST 2019" } ok: [local ] => (item=.....) => { "msg" : "Linux master 3.10.0-957.12.2.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Tue May 14 21:24:32 UTC 2019 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux" }
with_fileglob 关键字 描述: 是用来匹配文件名称的,我们可以通过”with_fileglob”关键字,在指定的目录中匹配符合模式的文件名;
比如:我们定义了一个列表,这个列表中只有一个值是一个路径,路径中包含一个通配符,如”/testdir/*”应该代表了/testdir目录中的所有文件;
基础示例:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 --- - hosts: local remote_user: root gather_facts: no tasks: - debug: msg: "{{ item }}" with_fileglob: - /tmp/demo*.??? - /root/* END
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ok: [local ] => (item=/tmp/demo1.txt) => {"msg" : "/tmp/demo1.txt" } ok: [local ] => (item=/tmp/demo2.txt) => {"msg" : "/tmp/demo2.txt" } ok: [local ] => (item=/root/with_dict.yml) => {"msg" : "/root/with_dict.yml" } ok: [local ] => (item=/root/with_subelement.yml) => {"msg" : "/root/with_subelement.yml" } ok: [local ] => (item=/root/with_fileglob.yml) => {"msg" : "/root/with_fileglob.yml" } ok: [local ] => (item=/root/with_sequence.yml) => {"msg" : "/root/with_sequence.yml" } ok: [local ] => (item=/root/with_random_choice.yml) => {"msg" : "/root/with_random_choice.yml" } ok: [local ] => (item=/root/with_file.yml) => {"msg" : "/root/with_file.yml" }