[TOC]
Servlet基础入门学习2
|[TOC]
0x01 Servlet 进阶
1.Cookies
1) 什么是Cookies?
英文翻译为饼干,它实际是一个信息记录程序,是服务器给客户端记录信息使用并且会存储在客户端上,用户可以随意的操纵(
实际上不安全);
2) Cookies有什么用?
由于HTTP协议请求是无状态的,客户端(多次)与服务器在通信的时候,服务器不知道该客户端是否曾经来访过,为了提高用户的体验以及收集用户的操作数据而使用(
实际上记录客户端上的用户使用信息)
3) Servlet中如何使用Cookies?
基础语法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30//1.在Servlet响应的时候进行添加Cookies,此时用户在收到响应头中会多一个set-Cookies字段;
response.addCookie(new Cookie(name, value));
//2.设置Cookies后客户端再下一次请求的时候会将该请求带代入,我们可以用Servlet请求进行获取;
Cookie[] cook = request.getCookies();
//防止出现空指针
if(cook != null)
{
for (Cookie cookie : cook) {
response.getWriter().append(cookie.getName() + " :" + cookie.getValue());
}
}
//3.Cookies失效期设置一般关闭浏览器则数据消失负值,而如果是正值则按照其设置秒数进行设置失效时间
Cookie age = new Cookie("age", "18");
age.setMaxAge(60 * 60 * 24 * 7); //单位秒,正值时间过期,负值时间关闭浏览器即失效;
age.setMaxAge(0); //删除Cookie
//4.设置新值(设置后任然需要进行提交)
age.setValue("2020");
//5.设置用于指定请求了指定的域名才会带上该Cookies
age.setDomain("127.0.0.1"); //只有在127.0.0.1该域才生效(可以区分内外网络)
//6.设置访问域名下的路径才会带有此Cookies
age.setPath("/");
//7.设置HttpOnly防止JS获取Cookies
age.setHttpOnly(true);
基础实例:获取用户上次登陆的时间; weiyigeek.top-1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89/**
* Servlet 设置 Cookies 验证
*/
public class Demo1 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8");
//1.内容回显
response.getWriter().append("Served at: ").append(request.getContextPath()+"<br/>");
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String value =request.getParameter("value");
//2.设置Cookies和有效期默认是7天
Cookie xm = new Cookie(name, value);
xm.setMaxAge(60 * 60); // 失效时间 1个小时
response.addCookie(xm);
System.out.println("设置的Cookie1: " + name + " = " + value);
//3.设置Cookies的有效期和HTTPOnly
Cookie age = new Cookie("age", "18");
age.setHttpOnly(true);
age.setDomain("127.0.0.1"); //只有在127.0.0.1该域才生效(可以区分内外网络)
age.setPath("/"); //设置域下访问的网页
age.setMaxAge(60 * 60 * 24 * 7); //单位秒,正值时间过期,负值时间关闭浏览器即失效;
age.setValue("2020"); //重新设置Cookie值
response.addCookie(age);
System.out.println("设置的Cookie2: " + age.getName() + " = " + age.getValue());
//3.获取请求的Cookies
Cookie[] cook = request.getCookies();
//防止出现空指针
if(cook != null)
{
for (Cookie cookie : cook) {
String cn = cookie.getName();
String cv = cookie.getValue();
response.getWriter().append(cn + " :" + cv + "<br>");
}
}
//4.显示最近访问的时间是什么时候;
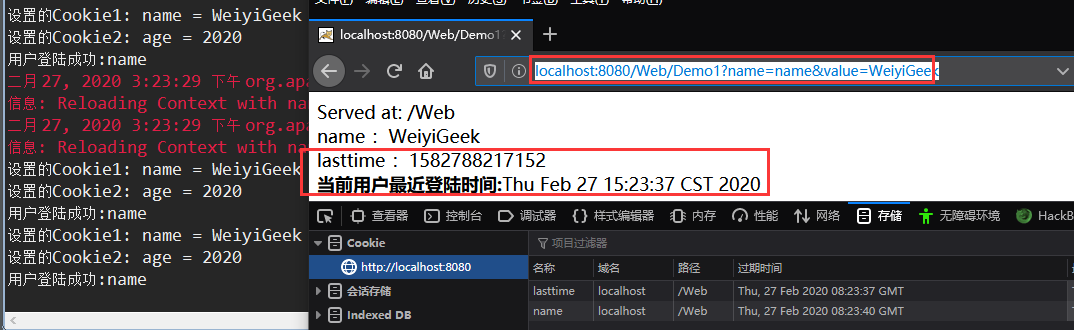
if("name".equals(name) && "WeiyiGeek".equals(value))
{
System.out.println("用户登陆成功:"+ name);
Cookie lastTime = until(cook,"lasttime"); //调用工具类进行查找
//判断用户是否首测登陆过
if(lastTime == null)
{
Cookie currentTime = new Cookie("lasttime",new Date().getTime()+"");
currentTime.setMaxAge(60*60);
response.addCookie(currentTime);
}else {
long lastVisitTime = Long.parseLong(lastTime.getValue()); //解析转换字符串为
response.getWriter().append("<b>当前用户最近登陆时间:</b>"+new Date(lastVisitTime));
lastTime.setValue(new Date().getTime()+""); //重置用户登陆的时间
response.addCookie(lastTime); //修改后重新响应提交
}
}else{
response.getWriter().append("<b>账号或者密码错误</b>");
}
}
//5.工具类:搜素
private Cookie until(Cookie[] userCook,String flag) {
if(userCook != null) {
for(Cookie ucook: userCook){
if(flag.equals(ucook.getName())){
return ucook;
}
}
}
return null;
}
//6.工具类,清除Cookies
private Boolean clearCookie(Cookie cook)
{
cook.setvalue("");
cook.setMaxAge(0);
response.addCookie(cook);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}
}
4) 总结补充
- 浏览器支持每台Web服务器有20个Cookie,总共有300Cookie,其中每一个Cookie的大小为4KB;
- 采用Cookie由于数据是存放在本地的容易出现安全等问题(比如Cookie盗用);
所以为了解决上面这些问题,采用了下面所学的Session方法进行记录用户Client的身份;
2.Session
1) 什么是Session?
描述:英文翻译为会话,它是基于Cookie的一种会话机制(技术),它不同于Cookie的是Session是服务端返回给客户端的标识,实际存储在服务器上,而在客户端浏览器里面Cookie会记录该Session值;
2) 有什么用Session?
描述:记录客户端多次请求访问标识并存储用户的信息,常使用在HTTP客户端与服务端的对话,并且保留指定时间段可以跨多个连接来着用户的页面请求,而服务端也可以采用多种方式维护会话如(使用Cookie或者重写URL);
在客户端访问Tomcat中网页的时候会生成一个Session并且添加到Cookie中即JSESSIONID=abc2FE1NT6GCYczGAQpcx
3) 如何使用Session API?
基础语法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19//1.获取用户的Session会话ID
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
String sessionid = session.getId();
response.getWriter().append("<h5>用户当前Session会话ID值 : " + sessionid + "</h5><br>");
//2.采用Session进行存值(在浏览器没有关闭后在没到失效时间时存放的值任然存在)
session.setAttribute("name", name);
session.setAttribute("pass", pass);
//3.获取Session中获取的值
session.getAttribute("name");
session.getAttribute("pass");
//4.移除值
session.removeAttribute("name");
session.removeAttribute("pass");
//5.关闭会话
session.invalidate();
基础示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67<%@page import="java.util.Map"%>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8"
pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Session</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Session 操作显示 </h1>
<p>
<!-- 简单的JSP定义说明 -->
<%! int a = 1234; %>
<% int b = 1024; %>
<b>a 值 = </b><%=a %> <br/>
<b>b 值 = </b><%=b %> <br/>
</p>
<!-- 登陆表单判断用户是否登录 -->
<!-- //3.获取会话设置的属性 -->
<% if (session.getAttribute("login") != "yes") { %>
<form action="Demo3" method="get">
用户名称: <input type="text" name="name"><br>
用户密码: <input type="password" name="pass"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<% } else { %>
<h4>尊敬的用户您已经成功登录了</h4> <p><a href="Demo3?action=logout">注销登陆</a></p>
<p>请选择购买的商品:</p>
<ol>
<li><a href='Demo3?id=1'>安全数据</a></li>
<li><a href='Demo3?id=2'>安全开发运维</a></li>
<li><a href='Demo3?id=3'>DevOps</a></li>
<li><a href='Demo3?id=4'>大型分布式网站架构</a></li>
<li><a href='Demo3?id=5'>安全威胁分析</a></li>
</ol>
<hr>
<p>您的购物车:<a href="#cart">go</a></p>
<div>
<table style="border: 1px black solid" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" rules="all" align="center">
<tr><th>商品名称</th> <th>购买数量</th></tr>
<% //6.从Session中获取到map;
Map<String,Integer> map = (Map<String, Integer>) session.getAttribute("cart");
//遍历Map
if (map != null)
{
for(String key: map.keySet()){
int value = map.get(key);
%>
<tr> <td><%=key %></td> <td><%=value %> 本</td> </tr>
<%
}
}else{
%>
<tr> <td>暂无</td> <td>暂无</td> </tr>
<%
}
%>
</table>
</div>
<br>
<p><a href="Demo3?action=del">清空购物车</a></p>
<% } %>
</body>
</html>
Java代码: weiyigeek.top-1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86package top.weiyigeek.sesssion;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
public class Demo3 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//0.获取JSP页面传递过来的参数
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String pass = request.getParameter("pass");
String action = request.getParameter("action");
String product = request.getParameter("id");
String[] productname = {"安全数据", "安全开发运维", "DevOps","大型分布式网站架构" , "安全威胁分析"};
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8");
if (name != null && pass != null ) {
if("admin".equals(name) && "123456".equals(pass)) {
//1.获取当前用户的Session会话值
String sessionid = request.getSession().getId();
response.getWriter().append("<br>用户登陆成功 <br>").append("当前 Session 会话值 : " + sessionid);
//2.设置登陆会话属性
request.getSession().setAttribute("login", "yes");
response.getWriter().append("<br><a style='color:red' href='index.jsp'>浏览商品</p>");
} else {
response.getWriter().append("<p style='color:red'>账号或密码错误!</p>");
}
}
//4.获取购物车存储的Session值
if (product != null ) {
int id = Integer.parseInt(product);
String idname = productname[id-1];
Map<String, Integer> map = (Map<String, Integer>) request.getSession().getAttribute("cart");
//首次
if(map == null) {
//存入Map对象到Session
map = new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>();
request.getSession().setAttribute("cart", map);
}
//判断是否存在该商品
if(map.containsKey(idname)) {
map.put(idname,map.get(idname)+1);
}else {
map.put(idname,1);
}
//界面跳转
response.getWriter().append("<br><b>添加到购物车成功!</b>");
response.getWriter().append("<p><a href='index.jsp'>返回商品页</a></p>");
response.getWriter().append("<p><a href='index.jsp?#cart'>我的购物车</a></p>");
}
//7.清空购物车即session值与会话清除
if ("del".equals(action)) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
session.removeAttribute("cart");
response.sendRedirect("index.jsp");
} else if ("logout".equals(action)) {
//Session 会话清除
request.getSession().invalidate();
response.sendRedirect("index.jsp");
}
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}
}
执行结果:访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/Web/login.jsp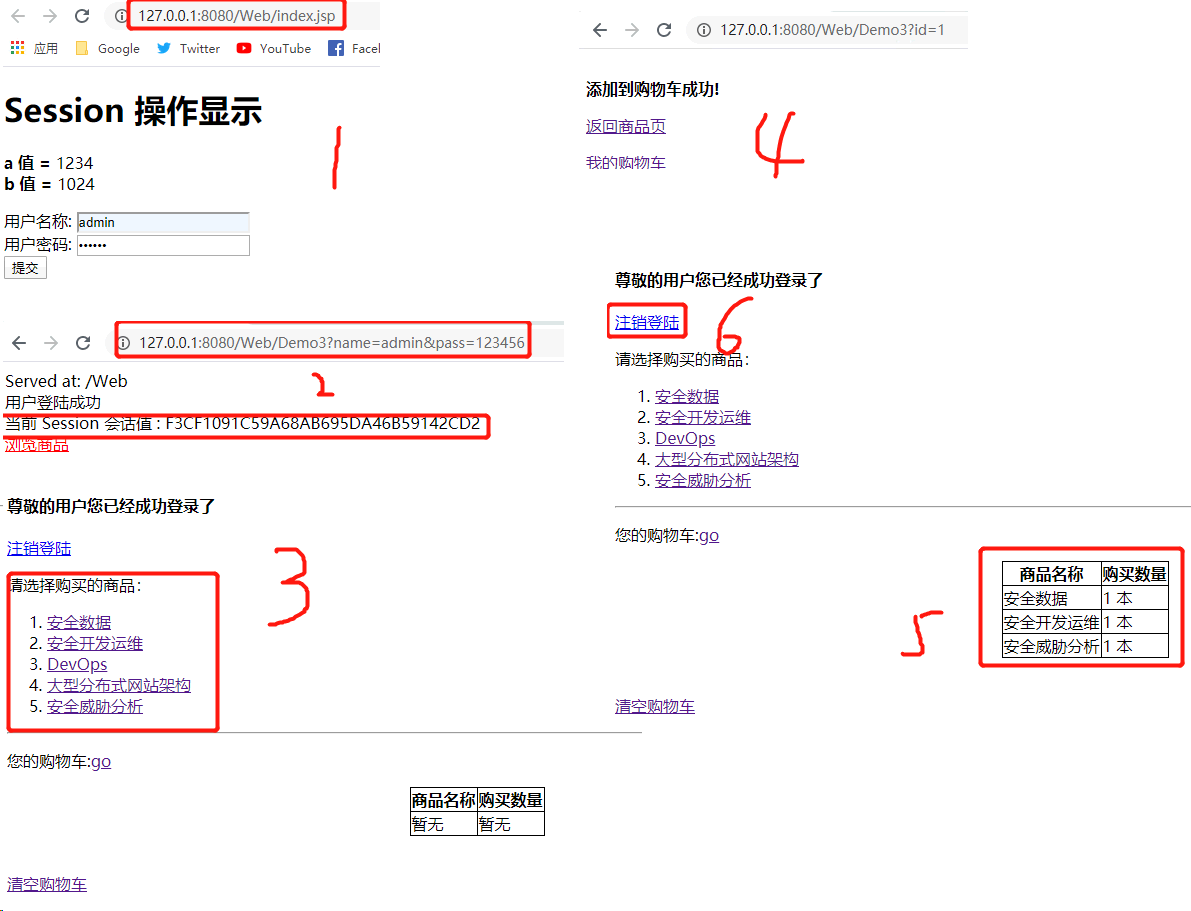
问题:Session何时创建又何时销毁?
1.创建:在Servlet中调用运行request.getSession(); //如果没有则进行创建当前会话ID
2.销毁:Session会在服务器应用或者系统关闭时候和会话到期(默认30分钟在tomcat的web.xml配置文件中设置)进行自动销毁由于Session是存放在内存之中,如果想做持久化则可以才Redis、Postgre等NOSQL数据库;
1 | <!--\Development\apache-tomcat-9.0.31\conf\web.xml --> |
0x01 补充说明
1.Servlet数量减少
描述:在我们的日常开发如果针对于一个用户数据的增删改查,以我们前面的方式则需要创建五个Servlet,但是在实际的开发中会产生代码冗余,所以我们为了减少Servlet的数量我们可以通过以下方式解决;
首先我们先来看看从客户端向服务端发起请求调用的几种方式:
- 1.通过表单
<form method="POST" action="BaseServlet?method=UserLogin"></form>发起服务端的请求 - 2.通过链接
<a href="BaseServlet?method=UserShow"></a>发起服务端的请求 - 3.通过Ajax异步请求服务端
1
2
3
4$(document).ready(function(){
$.ajax({url:"BaseServlet?method=UserVerity",async:true,success:function(result){ alert(result) }});
$.post("BaseServlet",{"method":"Userverity","user":"tom"},function(data){alert(data)});
});
基础示例1:(当功能模块较少时候可以这样做)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45public class ServletDemo01 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取客户端提交到服务端的method对应的值
String md=request.getParameter("method");
//定义变量,存放功能执行完毕之后要转发的路径
String path=null;
//通过判断md中不同的内容来决定本次功能
if("addStu".equals(md)){
path=addStu(request, response);
}else if("delStu".equals(md)){
path=delStu(request, response);
}else if("checkStu".equals(md)){
path=checkStu(request, response);
}else if("".equals(md)){
path="Index.html";
}
if(null!=path){
//服务端的转发
request.getRequestDispatcher(path).forward(request, response);
}
}
protected String addStu(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("添加学生");
return "/test.html";
}
protected String delStu(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("删除学生");
return "/test.html";
}
protected String checkStu(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("检查学生");
response.getWriter().println("DDDDDD");
return null;
}
}
Tips:该方式的弊端如果模块下功能较多,if(){}else{}语句过多;
基础示例2:(采用reflect反射机制利用字节码进行调用方法)
Base-Servlet : BaseServlet1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31/***
*
* @author WeiyiGeek
* @desc 工具类:自建一个Servlet基础类所有继承该类的Servlet都将执行重写后的Service方法
*/
public class BaseServlet extends HttpServlet {
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("BaseServlet - 被继承的基础Servlet中的Service方法");
//1.获取请求的操作的方法
String method = req.getParameter("method");
//2.定义转发路径
String redirection = null;
//3.获取当前的字节码对象
Class<? extends BaseServlet> clazz = this.getClass(); //此时获取的实际上是继承者的class即 UserOper.class
try {
//4.采用反射reflect形式获取到clazz的方法并且进行调用传入的指定方法
Method md = clazz.getMethod(method, HttpServletRequest.class, HttpServletResponse.class);
if (null != md)
redirection = (String) md.invoke(this, req, resp);
//5.当跳转路径不为空的时候返回的指定路径
if (null != redirection)
req.getRequestDispatcher(redirection).forward(req, resp);
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Servlet : UserOper1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19public class UserOper extends BaseServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public UserOper() {
super();
System.out.println("UserOper Servlet 构造方法!");
}
//Servlet中对用户操作的方法
public String addUser(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse reponse) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("addUser - 添加用户!");
return "Demo2/test.html";
}
public String showUser(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse reponse) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("showUser - 查看用户!");
return "Demo2/test.html";
}
}
执行结果:1
2
3
4
5
6UserOper Servlet 构造方法!
BaseServlet - 被继承的基础Servlet中的Service方法
addUser - 添加用户!
BaseServlet - 被继承的基础Servlet中的Service方法
showUser - 查看用户!
你好看友,欢迎关注博主微信公众号哟! ❤
这将是我持续更新文章的动力源泉,谢谢支持!(๑′ᴗ‵๑)
温馨提示: 未解锁的用户不能粘贴复制文章内容哟!
方式1.请访问本博主的B站【WeiyiGeek】首页关注UP主,
将自动随机获取解锁验证码。
Method 2.Please visit 【My Twitter】. There is an article verification code in the homepage.
方式3.扫一扫下方二维码,关注本站官方公众号
回复:验证码
将获取解锁(有效期7天)本站所有技术文章哟!

@WeiyiGeek - 为了能到远方,脚下的每一步都不能少
欢迎各位志同道合的朋友一起学习交流,如文章有误请在下方留下您宝贵的经验知识,个人邮箱地址【master#weiyigeek.top】或者个人公众号【WeiyiGeek】联系我。
更多文章来源于【WeiyiGeek Blog - 为了能到远方,脚下的每一步都不能少】, 个人首页地址( https://weiyigeek.top )

专栏书写不易,如果您觉得这个专栏还不错的,请给这篇专栏 【点个赞、投个币、收个藏、关个注、转个发、赞个助】,这将对我的肯定,我将持续整理发布更多优质原创文章!。
最后更新时间:
文章原始路径:_posts/编程世界/JavaWeb/1.Servlet/Servlet基础入门学习2.md
转载注明出处,原文地址:https://blog.weiyigeek.top/2020/2-26-302.html
本站文章内容遵循 知识共享 署名 - 非商业性 - 相同方式共享 4.0 国际协议
